Earned Value Management (EVM) is a robust system which integrates the project triple constraints of Time, report the project progress and makes forecasts which enables project managers to become more proactive.
The basic building blocks of EVM are;
- Planned Value (PV), which is also known as Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS)
- Earned Value (EV), which is also known as Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP)
- Actual Cost (AC), which is also known as Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP)
- Schedule Variance (SV) = PV-EV
- Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = EV/PV
- Cost Variance (CV) = EV-AC
- Cost Performance Index (CPI) = EV/AC
- Schedule Variance Percentage (SV%) = SV/PV*100
- Estimate at Completion (EAC) = AC+(BAC-EV)/CPI
- To Complete Performance Index (TCPI) = (BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC), where BAC is the total budget of the project.
82R-13 EVM Recommended practice elaborates the building blocks required to implement EVMS and are grouped into;
- Organization
- Planning, scheduling and budgeting
- Accounting guidelines
- Analysis and management reports
- Revisions and data maintenance
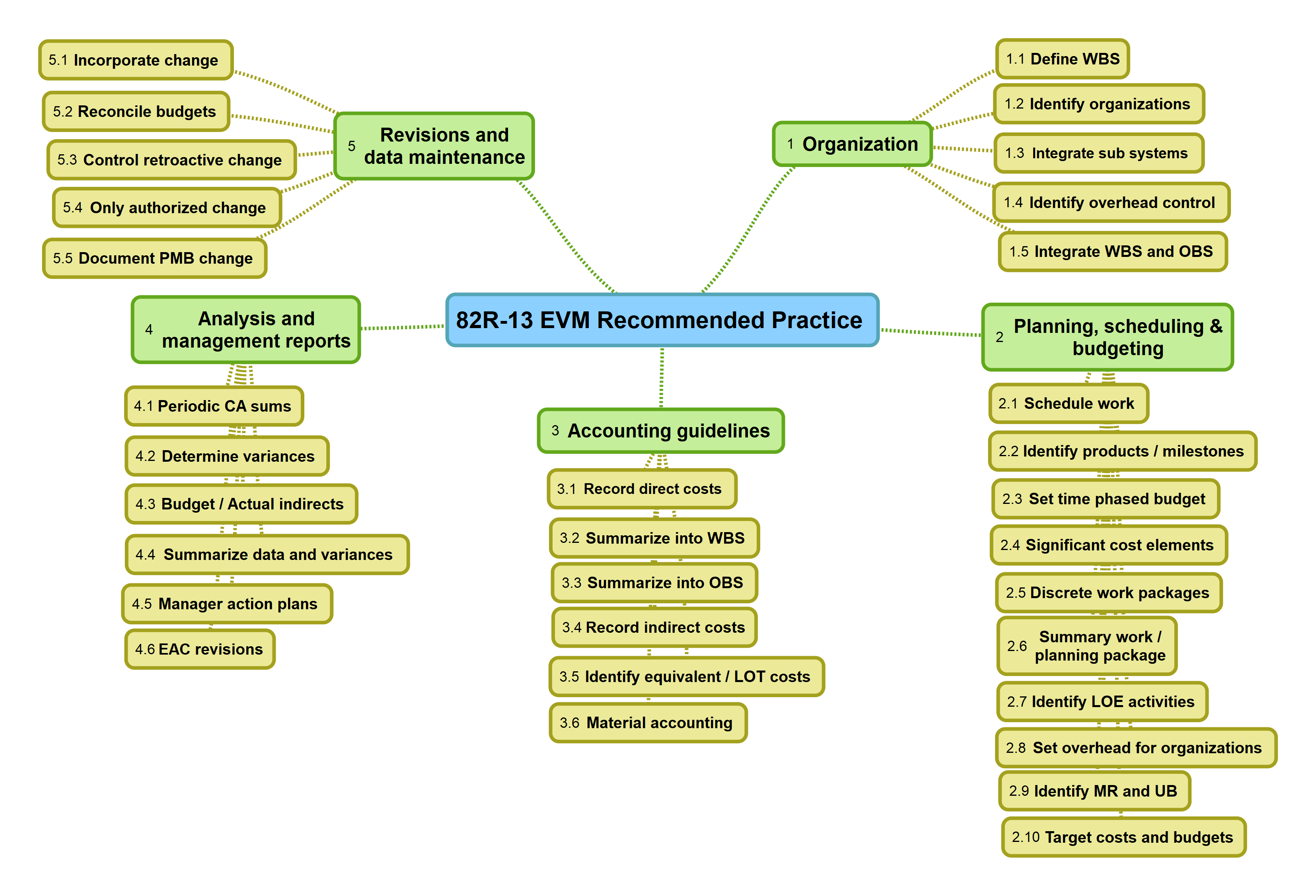
Organization
- Define WBS
- Identify organizations
- Integrate sub-systems
- Identify overhead control
- Integrate WBS and OBS
Planning, Scheduling & Budgeting
- Schedule work
- Identify products / milestones
- Set time phased budget
- Significant cost elements
- Discrete work packages
- Summary work / planning packages
- Identify LOE activities
- Set overhead for organizations
- Identify MR and UB
- Target costs and benefits
Accounting guidelines
- Record direct costs
- Summarize into WBS
- Summarize into OBS
- Record indirect costs
- Identify equivalent / LOT costs
- Material accounting
Analysis and management reports
- Periodic CA sums
- Determine variances
- Budget / actual indirects
- Summarize data and variances
- Manager action plans
- EAC revisions
Revisions and data maintenance
- Incorporate change
- Reconcile budgets
- Control retroactive change
- Only authorized change
- Document PMB change